LeNet
项目简介
1994 年深度学习三巨头之一的 Yan LeCun 提出了 LeNet 神经网络,这是最早的卷积神经网络。1998 年 Yan LeCun 在论文 "Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition" 中将这种卷积神经网络命名为 “LeNet-5”。LeNet-5 表明更好的模式识别系统可以建立在自动的学习上,更少的依赖手动设计的启发式模型。以字符识别为例,LeNet 表明手动选择的特征可以被更先进的直接在像素操作的学习机器取代。最早期的时候认为原始的数据非常多样并且丰富让模式识别被不能完全依靠手工建立一个准确的模式识别系统。所以,大部分的模式识别系统建立在自动学习技术和手工选择算法的结合。模式识别系统包含两个分开主要的模块,如图所示:
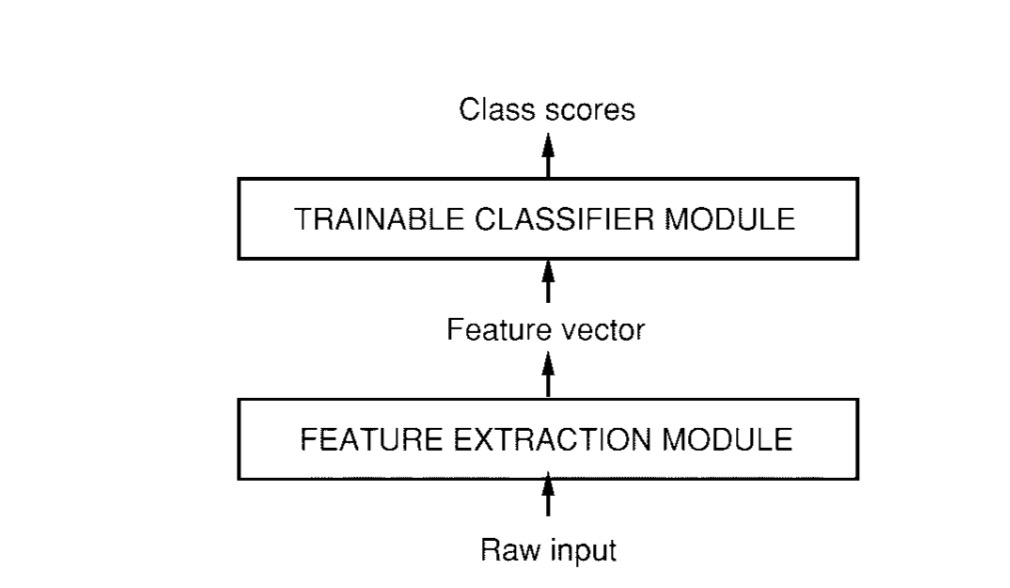
第一个模块,称为特征提取器,转换输入的数据,使他们可以被低维度的向量或者短字符表示。这样有两个好处:可以更加容易的匹配或者对比;虽然会进行转化和扭曲并不会改变输入的相对不变性。特征提取器包含大部分的前置知识,并且是针对任务的特定知识。它主要专注于模型设计方面的努力,因为它经常是完全手工设计的。另一方面,这个分类器通常用于普遍的目的,并且可以训练。这个过程的一个主要的问题是识别的准确率很大决定于设计者选择合适参数的能力。很不幸的是,这样使它成为一个让人畏惧的任务,因为这个任务必须为每一个新问题重新做一遍。
历史上,需要合适的特征提取器的需求来自分类器的学习技术受限于比较容易分类的低维度空间。在过去的十年中,有三个事实改变了这个观点。第一,可以获得很便宜的高速算数计算单元允许使用更多的蛮力计算而不是算法优化。第二,对于有巨大市场和广泛兴趣的问题可以获得大数据库,比如说手写数字识别,让设计者可以依赖更多的真实数据,更少使用手动调整的特征提取器来建立识别系统。第三,也是最重要的事实就是可以获得高性能机器学习技术从而可以处理高维度输入,并且可以在输入大量数据集的时候生成复杂的决策函数。
Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=726791
论文下载链接:
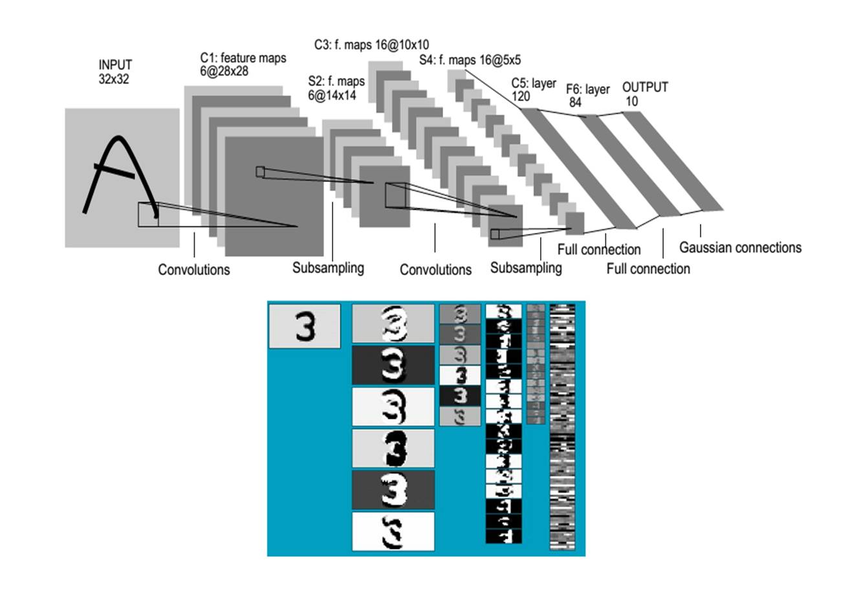
Architecture of LeNet-5 (Convolutional Neural Networks) for digit recognition
数据处理
同卷积神经网络中的 MNIST 数据集处理方法。
TensorFlow 卷积神经网络手写数字识别数据集介绍
http://www.tensorflownews.com/2018/03/26/tensorflow-mnist/
模型实现
经典的卷积神经网络,TensorFlow 官方已经实现,并且封装在了 tensorflow 库中,以下内容截取自 TensorFlow 官方 Github。
models/research/slim/nets/lenet.py https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/lenet.py
import tensorflow as tf
slim = tf.contrib.slim
def lenet(images, num_classes=10, is_training=False,
dropout_keep_prob=0.5,
prediction_fn=slim.softmax,
scope='LeNet'):
end_points = {}
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'LeNet', [images]):
net = end_points['conv1'] = slim.conv2d(images, 32, [5, 5], scope='conv1')
net = end_points['pool1'] = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], 2, scope='pool1')
net = end_points['conv2'] = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [5, 5], scope='conv2')
net = end_points['pool2'] = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], 2, scope='pool2')
net = slim.flatten(net)
end_points['Flatten'] = net
net = end_points['fc3'] = slim.fully_connected(net, 1024, scope='fc3')
if not num_classes:
return net, end_points
net = end_points['dropout3'] = slim.dropout(
net, dropout_keep_prob, is_training=is_training, scope='dropout3')
logits = end_points['Logits'] = slim.fully_connected(
net, num_classes, activation_fn=None, scope='fc4')
end_points['Predictions'] = prediction_fn(logits, scope='Predictions')
return logits, end_points
lenet.default_image_size = 28
def lenet_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0):
"""Defines the default lenet argument scope.
Args:
weight_decay: The weight decay to use for regularizing the model.
Returns:
An `arg_scope` to use for the inception v3 model.
"""
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1),
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu) as sc:
return sc
模型优化
下一篇将会介绍 AlexNet 。